Treatment of Mary Huntoon’s Kansas City, Kansas Grain Elevators, an Etching: Part 2
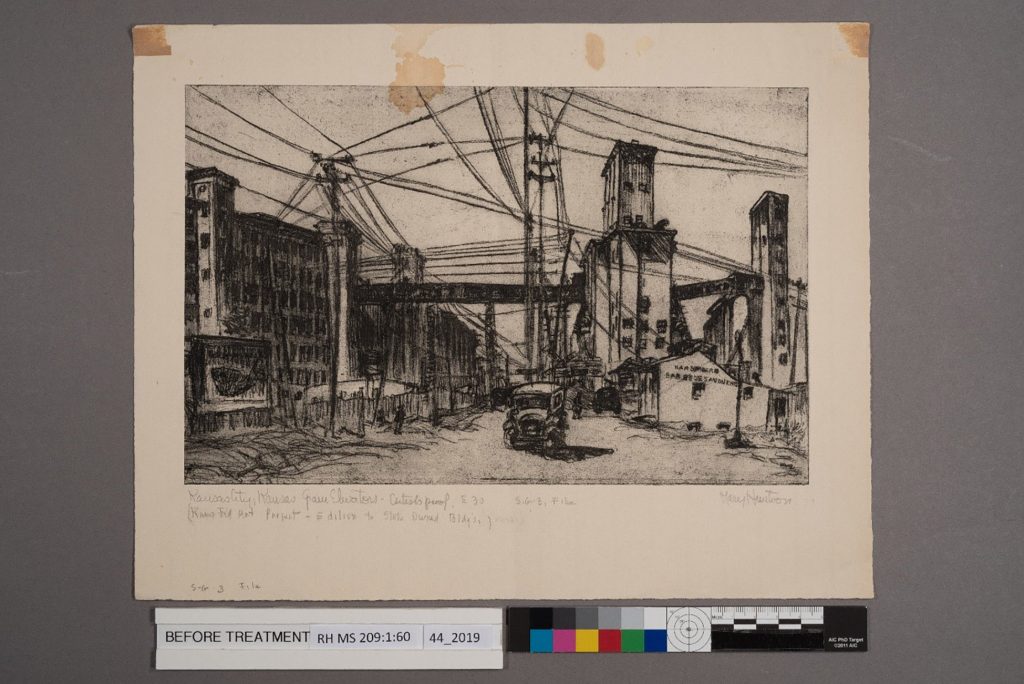
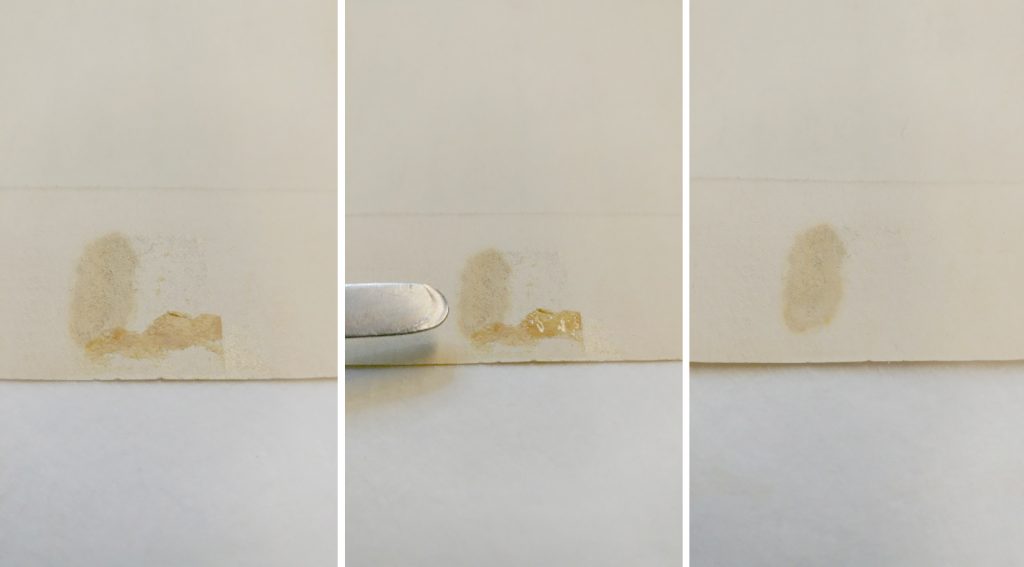
May 19th, 2020In the first installment of this two part blog series, the Kansas artist, Mary Huntoon, was introduced. We shared how her print, Kansas City, Kansas Grain Elevators, was prepared for an overall washing treatment in order to reduce several dark brown stains along the top edge that interrupted the image area and created bulging in the surface.
Before any washing treatments are performed on works on paper, all media are tested with the proposed washing solutions to ensure their stability. The surface is also checked for any areas where the print may have been previously restored, or even re-touched by the artist with another material that might be water-soluble. I carefully examined the print under magnification during testing in order to make sure the ink and paper were safe for washing. Everything checked out, so I was ready to start the washing step.
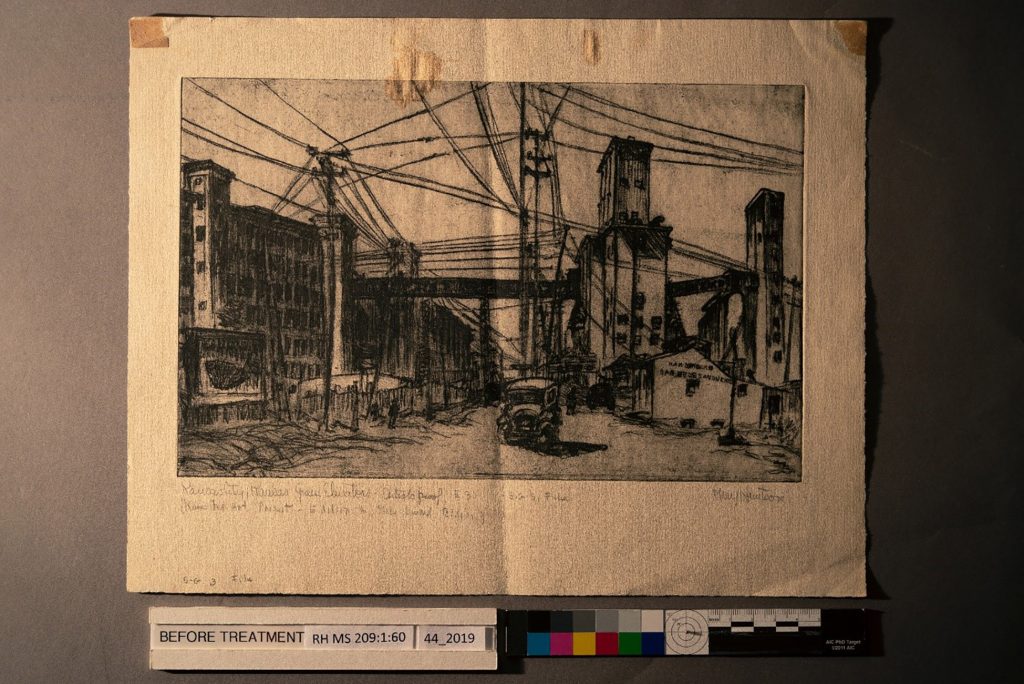
Prior to washing, the print was gently surface-cleaned and the brown paper attachments were removed. You can read more about these steps in the first blog post about this treatment.
Before a work on paper is placed into a bath, the entire object must slowly undergo a humidification step. This helps to relax the paper and the media and prevents aggressive swelling. Then the object is gently sprayed with deionized water using a fine mist attachment in order to fully saturate it. This step-wise procedure ensures a gentle transition for the object into the bath.
The print was washed in successive baths of pH-adjusted deionized water and air-dried. I examined the print once again to assess the progress of the washing step. The stains had noticeably lessened, but they were still quite visible, and I decided to test another stain reduction technique.
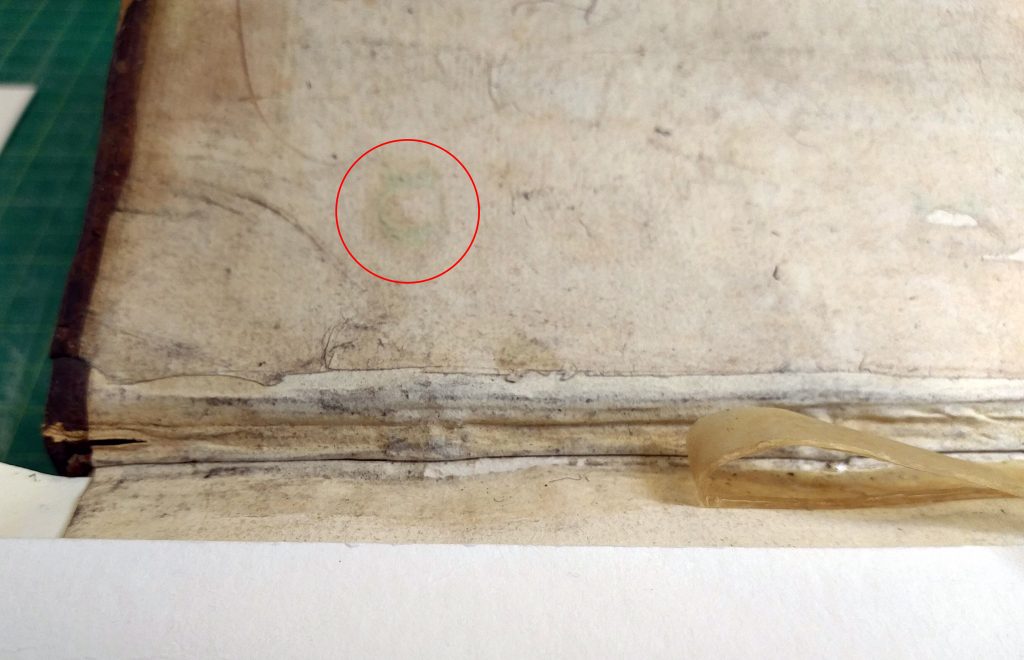
Using a small brush, I gently introduced very small applications of a dilute reducing bleach to the stained areas. This reduced the stain to an almost undetectable level. Then the bleach was fully rinsed with additional baths of pH-adjusted deionized water. I used an ultraviolet lamp to check to see that all the bleach, which fluoresces under ultraviolet radiation, was rinsed away.

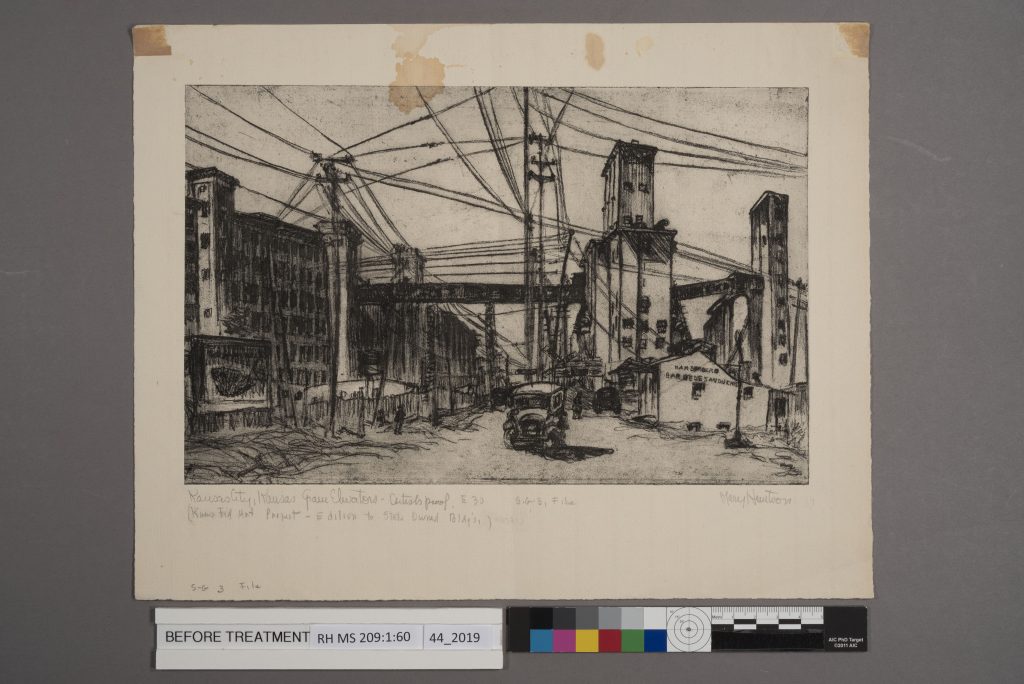
After the stain reduction and overall washing was complete, it was time to address a few structural concerns. Weak creases in the upper corners made the print vulnerable to breakage and tearing, so I reinforced them using Japanese paper applied with wheat starch paste we make in our conservation lab. Instead of cutting the Japanese paper, it is wetted and torn. This torn edge makes use of the long kozo fibers in the paper and creates a strong mend that integrates well into the paper. After all the mends and reinforcements were complete, the print was humidified a second time and flattened between thick felts. Pressing between felts helped to remove planar distortions along the edges, while also maintaining the plate mark of the etching.
Now that the treatment is complete, the print is ready to be returned to the collection where it can be safely examined by visitors to the Kenneth Spencer Research Library.
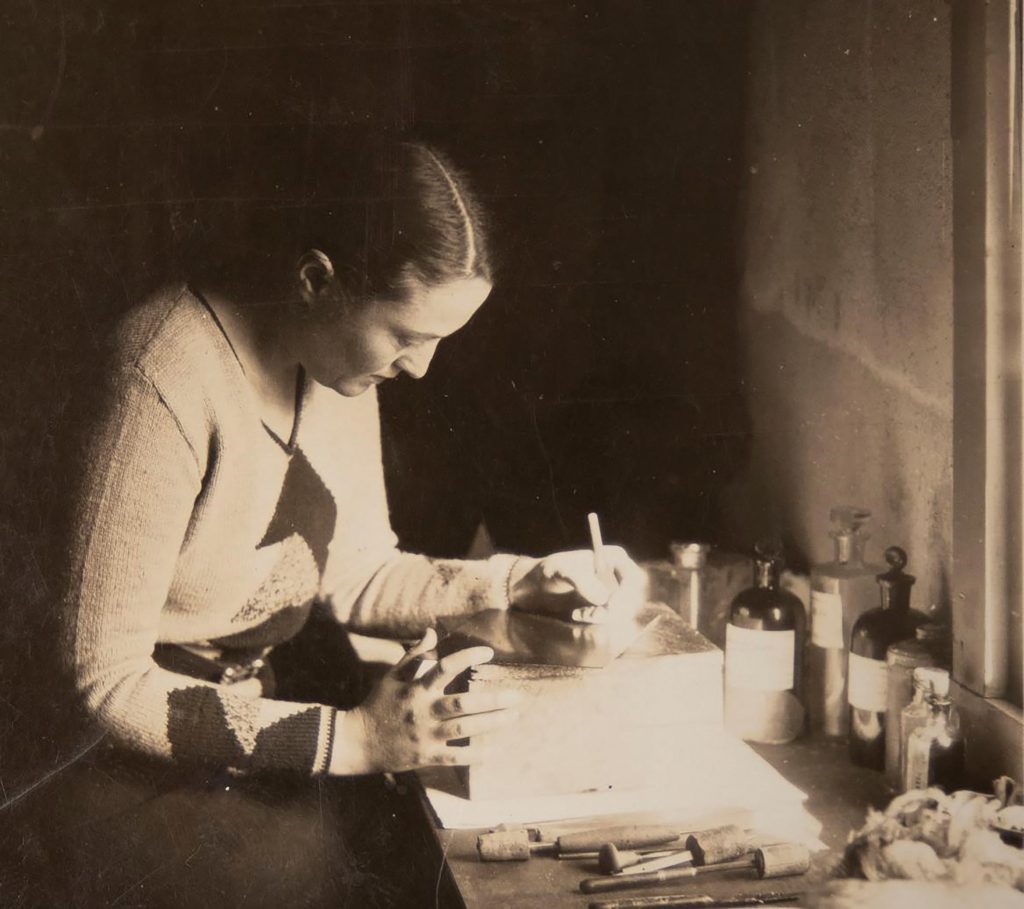
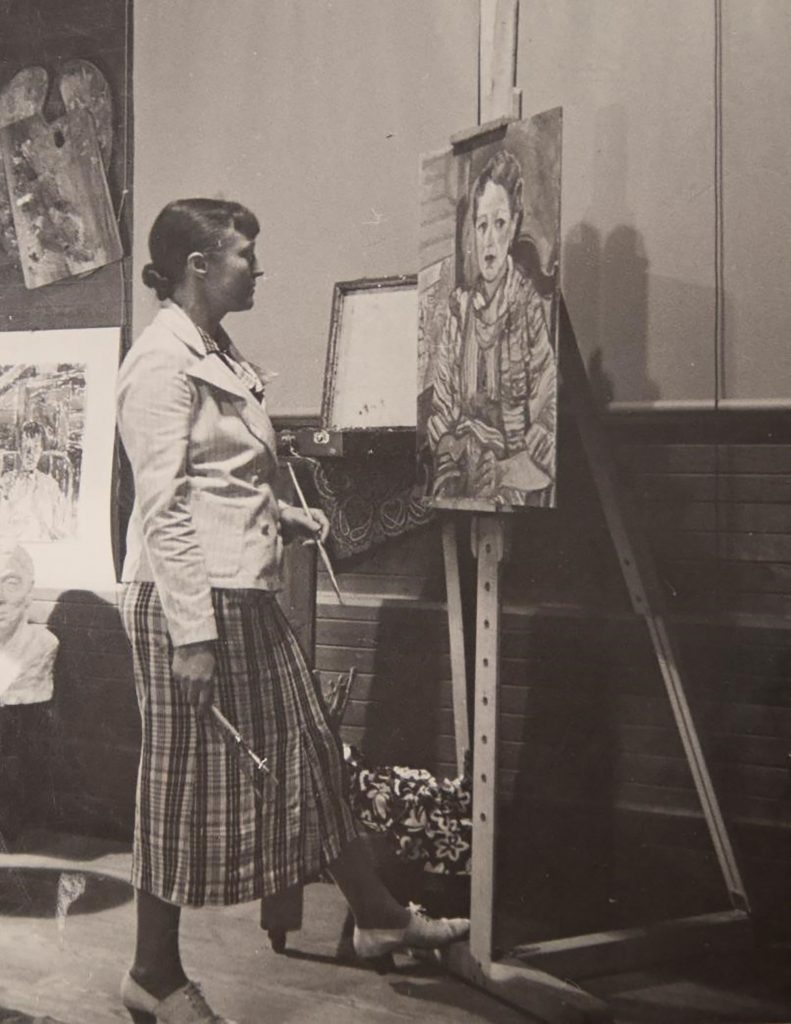
The Kenneth Spencer Research Library is home to the collection of papers and original artwork by Kansas artist and art therapist, Mary Huntoon (1896 – 1970). As part of a collaborative initiative between KU Libraries and the Spencer Museum of Art, funded by the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation, many of the prints, drawings, and watercolors by Huntoon will be treated.


Jacinta Johnson, Associate Conservator, Mellon Initiative