That’s Distinctive!: Cottonwood Falls, Kansas, School Photos
March 29th, 2024Check the blog each Friday for a new “That’s Distinctive!” post. I created the series because I genuinely believe there is something in our collections for everyone, whether you’re writing a paper or just want to have a look. “That’s Distinctive!” will provide a more lighthearted glimpse into the diverse and unique materials at Spencer – including items that many people may not realize the library holds. If you have suggested topics for a future item feature or questions about the collections, feel free to leave a comment at the bottom of this page.
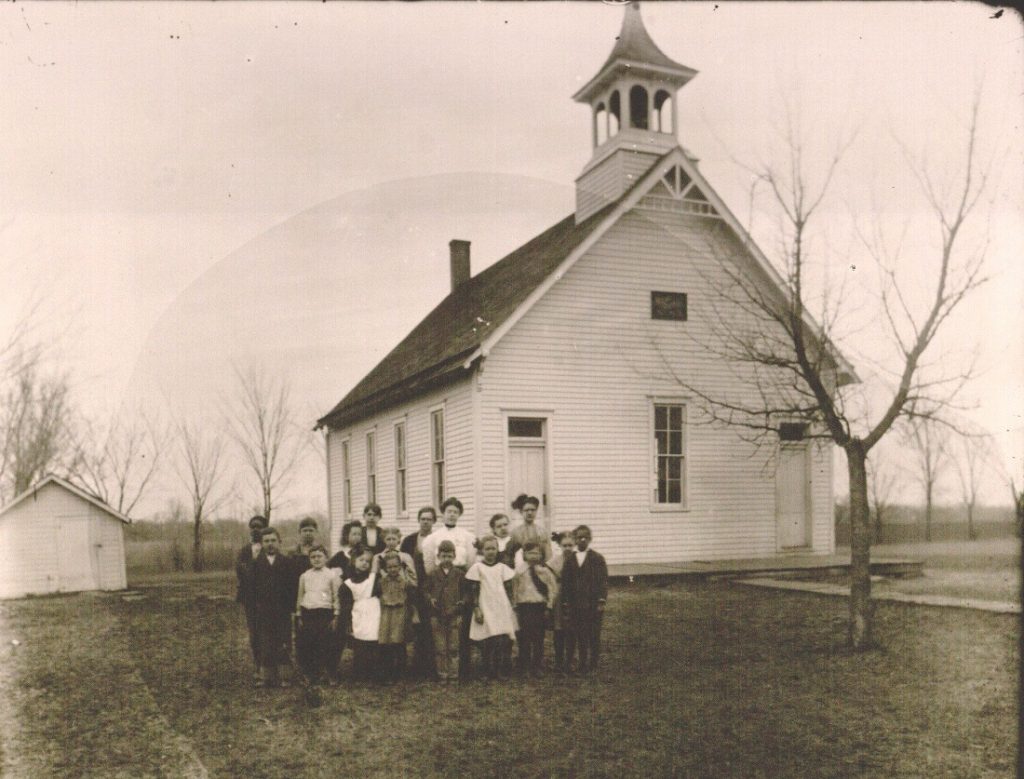
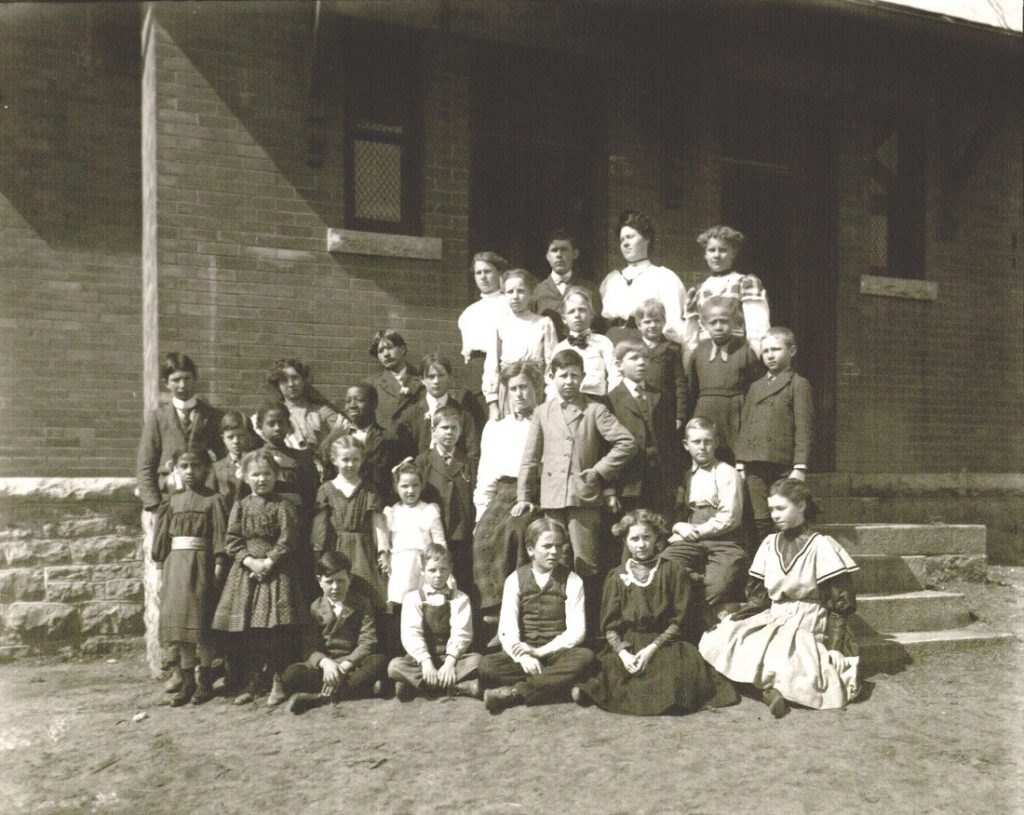
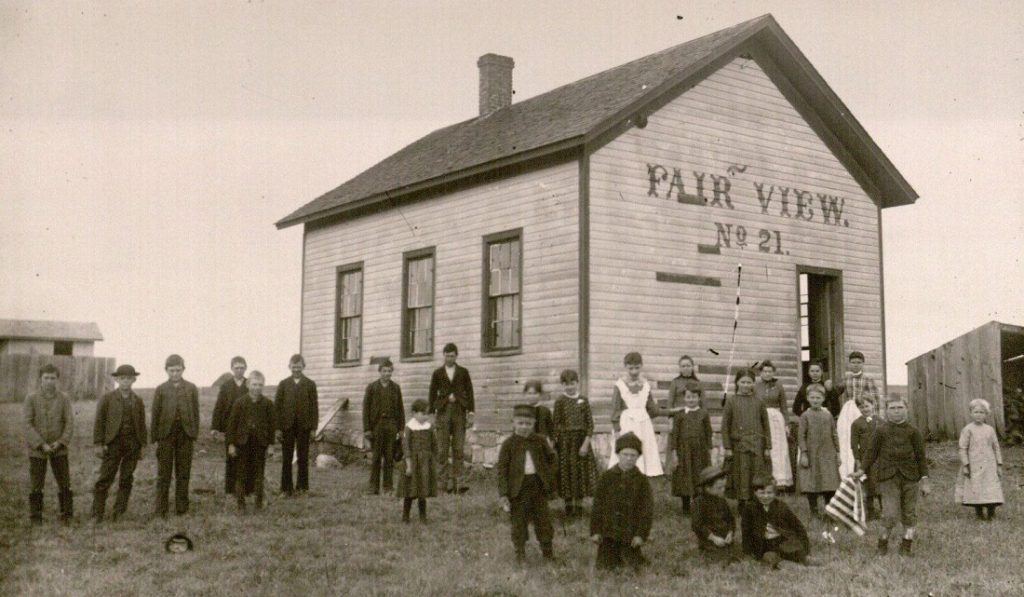
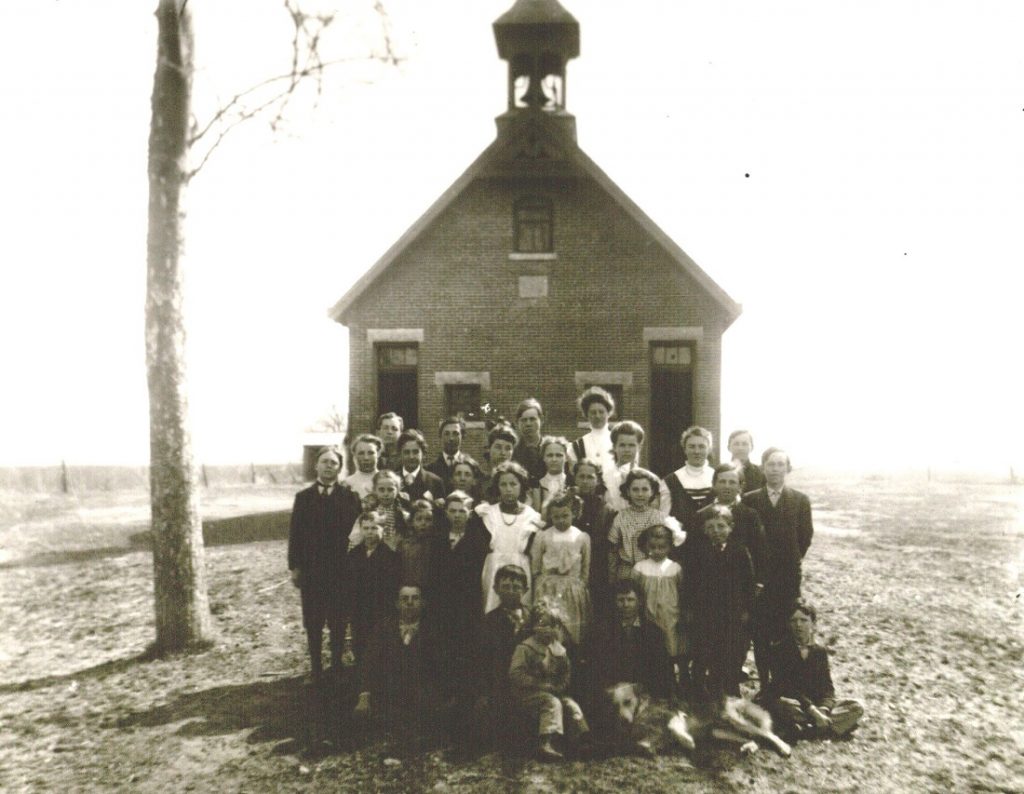
This week on That’s Distinctive! I am sharing a glimpse into the activities of a Cottonwood Falls, Kansas, school in the early twentieth century via a 1918 scrapbook of photographs. Although the scrapbook is titled “eighth-grade class snapshots,” some images include other grades such as fifth and seventh. Other photos show the inside of the classrooms. There are also class portraits throughout the scrapbook. In the back of the book is a May 1918 copy of the City School Monitor, which was “edited and published by the pupils of the City School.” The one included in the book is volume 2, number 3, and it includes “local school news.” Some topics covered are student illnesses, teacher departures, and new students. One notable topic is the small comment that “Willie Ellis, who was a member of the fourth grade, was struck by lightning while fishing near Buck Creek May 4th.”
Cottonwood Falls, Kansas, is nestled in the heart of the Flint Hills in Chase County. With a population of approximately 850 people, Cottonwood Falls is the largest “city” in Chase County. Though small, the town boasts art galleries, antique shops, a historical museum, and many dining experiences. It is also home to “the oldest consecutively utilized courthouse west of the Mississippi.”

Tiffany McIntosh
Public Services