Manuscript of the Month: The Making of a Medieval Codex
October 27th, 2020N. Kıvılcım Yavuz is conducting research on pre-1600 manuscripts at the Kenneth Spencer Research Library. Each month she will be writing about a manuscript she has worked with and the current KU Library catalog records will be updated in accordance with her findings.
We have very little information about the past history of Kenneth Spencer Research Library MS C195. When, where and by whom it was made are unknown. This is not surprising; the origins of many medieval manuscripts are uncertain. Scholars utilize different evidence to determine the circumstances in which a manuscript was produced as well as its history since its production. The only hint about the past of MS C195 comes from a note dated to 1841 glued onto the front pastedown according to which the manuscript previously belonged to the library of the Charterhouse of Montrieux (Chartreuse Notre-Dame de Montrieux) in Méounes-les-Montrieux in southeastern France. This Carthusian monastery that was originally built in 1137; yet even if MS C195 was in their library at some point, it does not mean that it was made there, although it could suggest the general region in which it was created.
MS C195 contains a copy of Petrus Riga’s Aurora, a verse commentary on the Bible. Also known as Peter Riga (approximately 1140–1209), Petrus was a canon of the Cathedral of Notre Dame of Reims and later a Canon Regular of the Order of St Augustine at St Denis, also in Reims, France. It is thought that the Aurora was written over a long period of time at the end of the twelfth century, between 1170 and 1200. The modern editor of the Aurora, Paul E. Beichner, argues that there were three different editions of the work, all by Petrus Riga, over this thirty-year period as well as two later redactions by Petrus’s disciple, Aegidius of Paris (also known as Egidius or Gilles de Paris, approximately 1160–1223/1224). The text as it is contained in MS C195 is a copy of the third edition of the Aurora except that the beginning is missing and it does not include the chapter titled “Recapitulationes.”
Identifying the text contained in a manuscript only takes us so far in terms of understanding and appreciating the book as an object. On the other hand, a detailed physical examination, although it will not provide all the answers about the origin of a manuscript, allows us to discover the circumstances in which the manuscript was produced and used. When it comes to understanding the history of a manuscript, codicology, the study of manuscripts as physical objects, is as vital as the study of the texts contained in the manuscripts. When we look at MS C195, the first thing to be noticed is that the manuscript is no longer in its original binding. The current binding, which is probably early modern, is leather over paper boards, with both of its covers and spine blind-tooled. That the manuscript was rebound at some point requires one to be more careful when conducting an examination of the bookblock as there might be alterations such as added leaves or reorganized gatherings that were introduced—both knowingly and unintentionally—during the rebinding.

MS C195 is a parchment manuscript. As we leaf through the manuscript, we see that some leaves are thicker than others, some have yellower tint than others, several leaves have holes and cuts, and dozens of stubs are visible in the gutters. Furthermore, there are at least a few leaves that are palimpsests, still bearing visible traces of former writing on them. The variety of thickness and color of the parchment may indicate that these were made of different animal skins or prepared at different times or in different ways. Holes and cuts in the parchment usually occur during the preparation of animal skins, especially when hair was being scraped off with a knife. The existence of stubs mean smaller, single parchment leaves were added or inserted into the gatherings instead of using bigger sheets of parchment (or, in some cases that the existing leaves were cut out). Taken together with the existence of palimpsests in the manuscript, these features all indicate that the manuscript was made at a time and a place in which the resources were limited and that the scribe (or the compiler) of the manuscript made use of whatever material was available.


In most cases, the imperfections in the parchment in MS C195 are found in the margins. Other times, when it was not possible to arrange the leaves so that the holes and the cuts remained in the margins, the scribe worked around these defects to complete the text, as seen, for example, on folio 107v and folio 108v. As for the stubs visible in the manuscript, all of these seem to be additions of single leaves to the gatherings made by the scribe as part of the original design. As it stands, MS C195 consists of 233 parchment leaves arranged in 31 quires. There are some signs of rearrangement. For example, the first two leaves of the original second gathering (now the third quire) were dismembered and are missing, and the last two leaves of the same gathering were misbound (now the second quire). Nevertheless, most of the quires seem to be intact and in their original order.
Although it is not particularly complex, the collation of the manuscript displays the resourcefulness of the scribe. The collation formula of MS C195 is as follows:
14 + 24 (wants 1 and 2) + 34 + 48 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 58 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 610 (3 and 8 are singletons) + 78 (3 and 6 are singletons) + 88 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 98 + 1010 +1112 + 1 leaf after 10 + 128 + 1 leaf after 3 + 13-148 + 156 + 1 leaf after 1 + 168 + 178 (5 and 7 are singletons) + 188 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 19-208 + 218 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 228 + 238 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 242 + 1 leaf after 1 + 25-278 + 288 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 298 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 308 (2 and 7 are singletons) + 314 (wants 4).
Even for the trained eye, such a collation formula might be intimidating. Furthermore, as detailed as this formula is, it still provides limited information as to the materiality of the manuscript and how the manuscript was actually put together. As it is seen in the collation formula, the majority of the quires are quaternions, that is, gatherings of 8 leaves which are usually made up of 4 folded sheets. In MS C195, however, 11 of the 22 quaternions are formed by putting together 3 folded sheets, which make up six conjoint leaves, and two single leaves. In the seventh quire, the third and the sixth leaves are singletons, and in the remaining 10 quires the second and the seventh leaves; but the arrangement of the leaves with respect to sewing are not always the same.
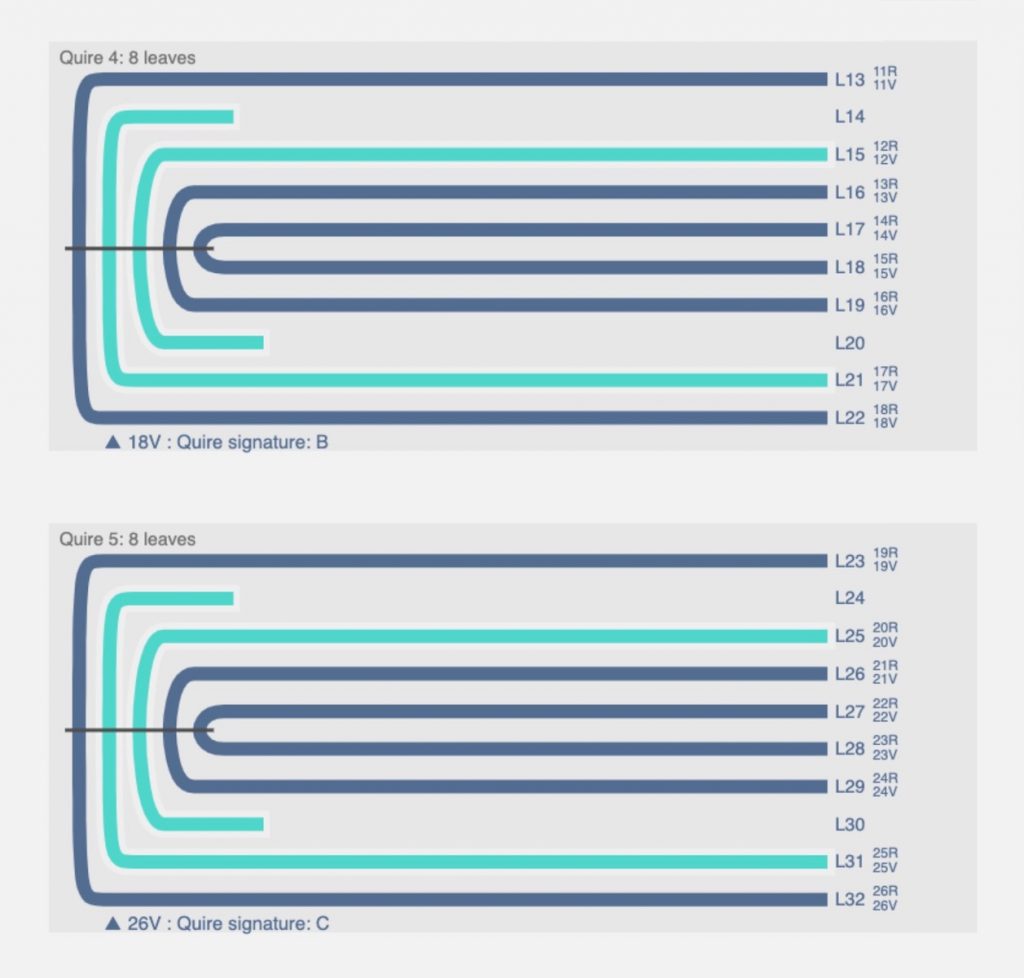
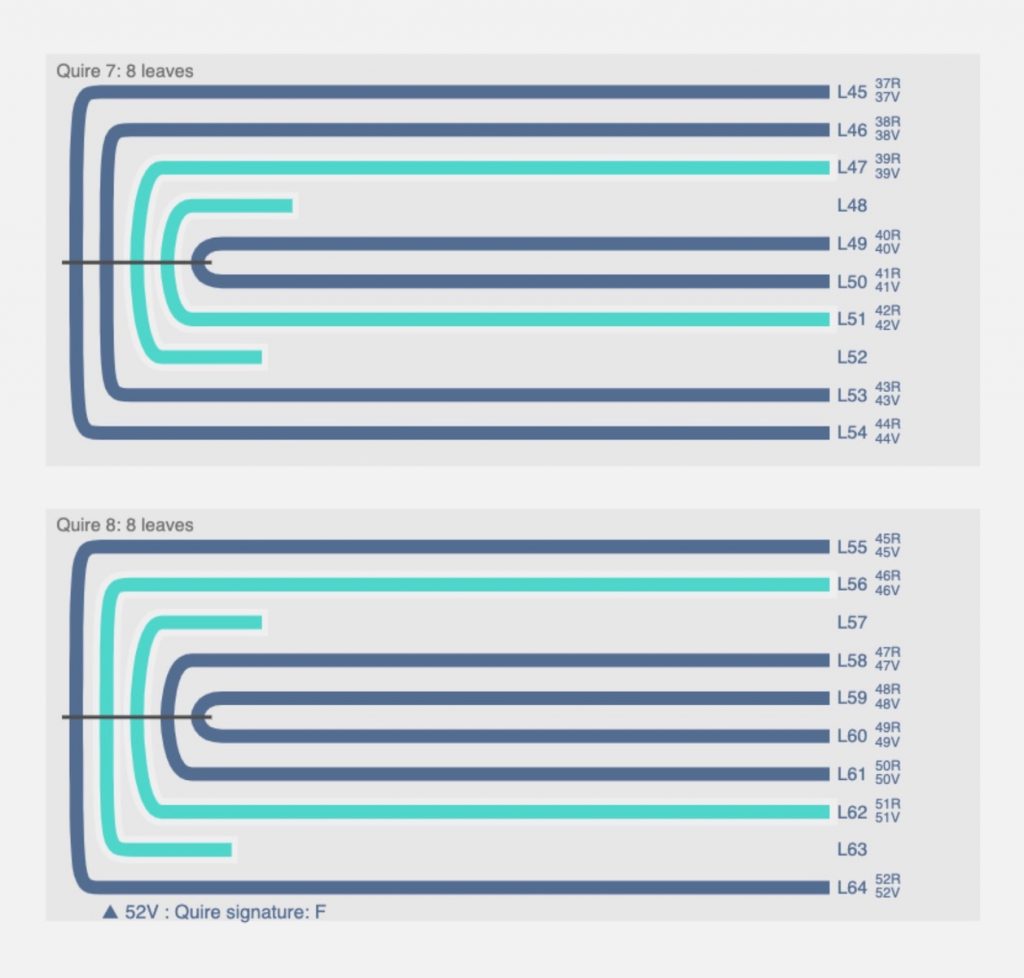
A visual representation of the collation of the manuscript provides more information as to the arrangement of the leaves in each quire. In the visualization, it is seen clearly that even though quires 4, 5 and 8 are formulated in the same way, the manner in which they appear in the manuscript is not the same. An interactive version of the full collation of MS C195 can be viewed on VisCodex. Part of Digital Tools for Manuscript Study developed by the University of Toronto Libraries Information Technology Services and the Old Books New Science Lab at the University of Toronto, VisCodex is a web application based on VisColl, a system for modelling and visualizing collations of manuscripts created by Dot Porter and Alberto Campagnolo.
Writing collation formulas or indeed creating visualizations for collations is not a recent development, but as it is the case here, digital tools dedicated to manuscript studies can help us understand the physicality of artefacts better and share our knowledge with wider audiences. There are several other codicological aspects of MS C195, such as ruling and pricking, that can be examined and visualized in a similar manner to its collation in order to see what kinds of patterns can be detected. Findings of these examinations in turn can enable scholars to compare MS C195 with similar manuscripts, and perhaps even one day to pinpoint its date and place of production.
The Kenneth Spencer Research Library purchased the manuscript from Bernard M. Rosenthal Inc. in January 1969, and it is available for consultation at the Library’s Marilyn Stokstad Reading Room when the library is open.
- Edition of Petrus Riga’s Aurora: Aurora: Petri Rigae Biblia Versificata. A Verse Commentary on the Bible. Ed. Paul E. Beichner. 2 vols. Publications in Mediaeval Studies 19. Notre Dame, IN: University of Notre Dame Press, 1965.
N. Kıvılcım Yavuz
Ann Hyde Postdoctoral Researcher
Follow the account “Manuscripts &c.” on Twitter and Instagram for postings about manuscripts from the Kenneth Spencer Research Library.


