Improving the Physical Environment in Spencer Library: The Third Visit from Image Permanence Institute
December 12th, 2018KU Libraries recently hosted Christopher Cameron and Kelly Krish, consultants from Image Permanence Institute (IPI), for their third and final visit as part of the planning grant we were awarded from the National Endowment for the Humanities, under the Sustaining Cultural Heritage Collections program. The purpose of the grant is to work with our environmental consultants to study the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system in Spencer Research Library in order to more sustainably preserve our collections.
On December 4-5, 2018, Chris and Kelly met with members of the KU team representing Facilities Services, Campus Operations, KU Libraries, and Facilities Planning and Development. We first met to discuss building and mechanical system updates since their visit in April, such as the opening of a new conservation lab and work on windows in Spencer Library’s North Gallery. In addition, we talked about weather conditions in Lawrence, Kansas, during the spring, summer, and fall.
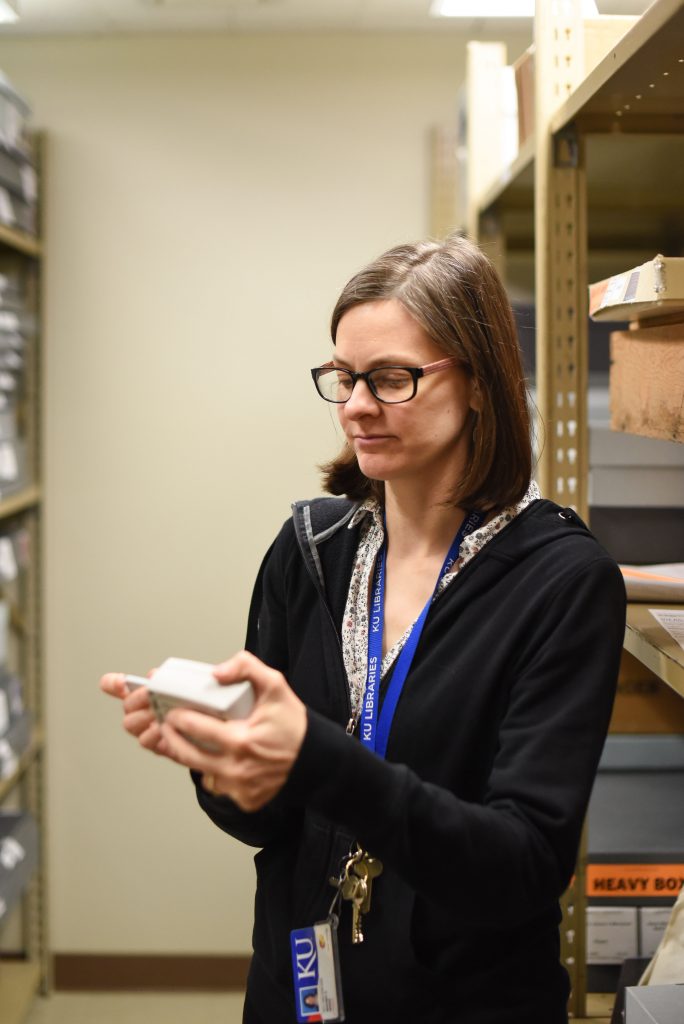
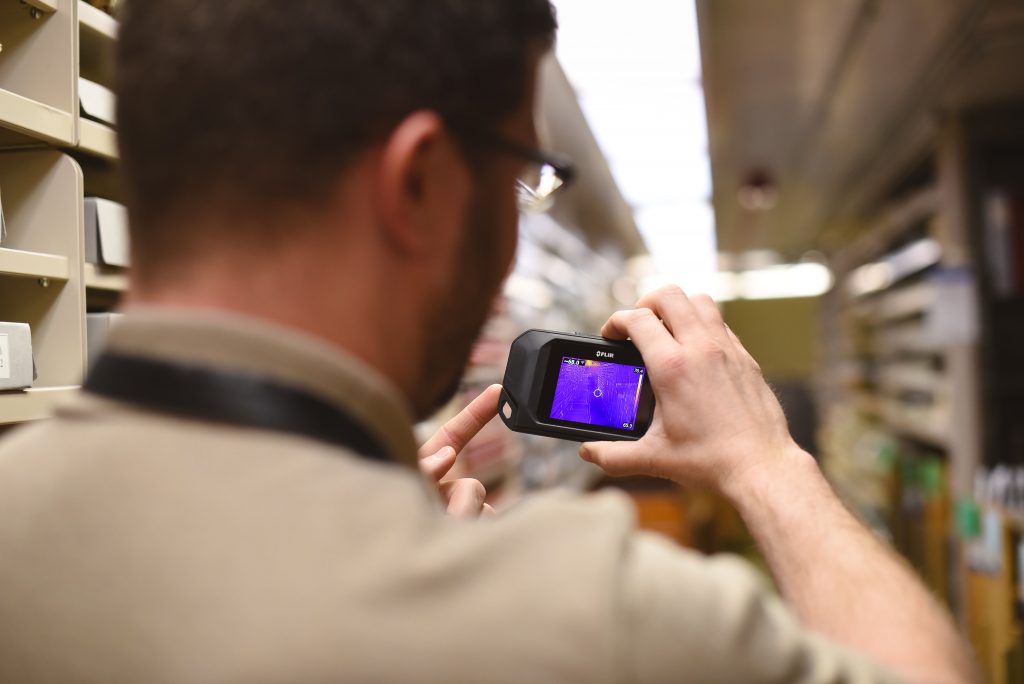
As in past visits, the consultants collected data from dataloggers placed in the mechanical system, vents in the collections stacks, and in open spaces in the stacks. They then spent time analyzing the data and searching for anomalies that should be addressed.

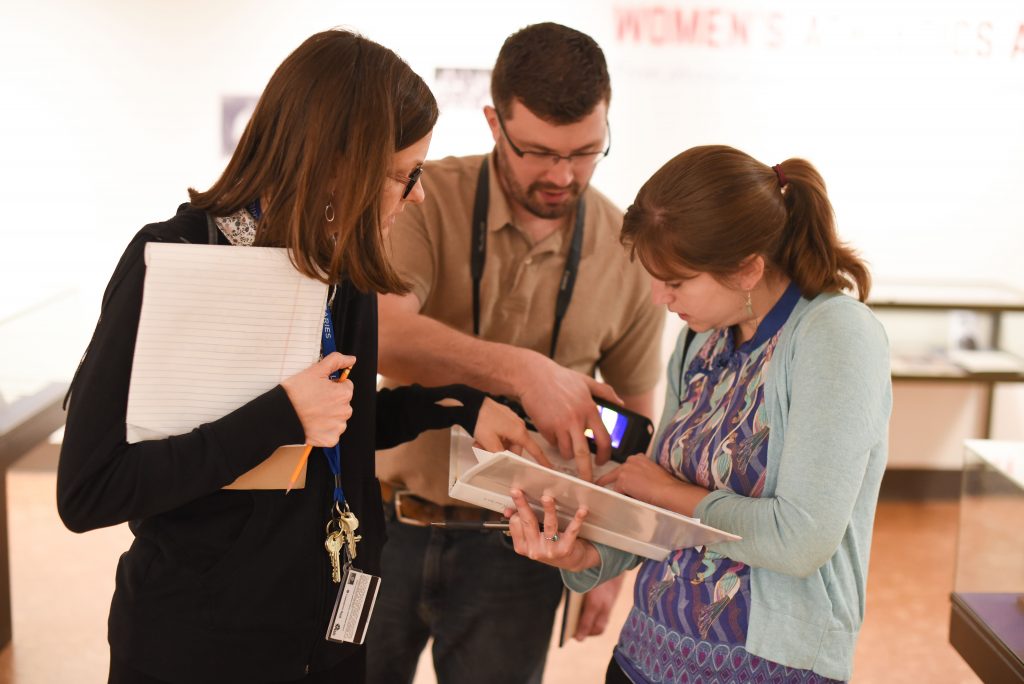
Chris Cameron and Kelly Krish check for air flow from a vent
in the new conservation lab. Click image to enlarge.
On the second day, the consultants met with the KU grant team to discuss the conclusions that resulted from a year of studying Spencer Research Library. Chris and Kelly referred to climate data gathered over a year’s time in eClimate Notebook. We also discussed ways to improve the sustainability of our system, which currently consumes too much energy. The consultants showed us architectural drawings for the airflow throughout the building in order to ponder how our HVAC system might be updated to provide separate zones for collections and people.
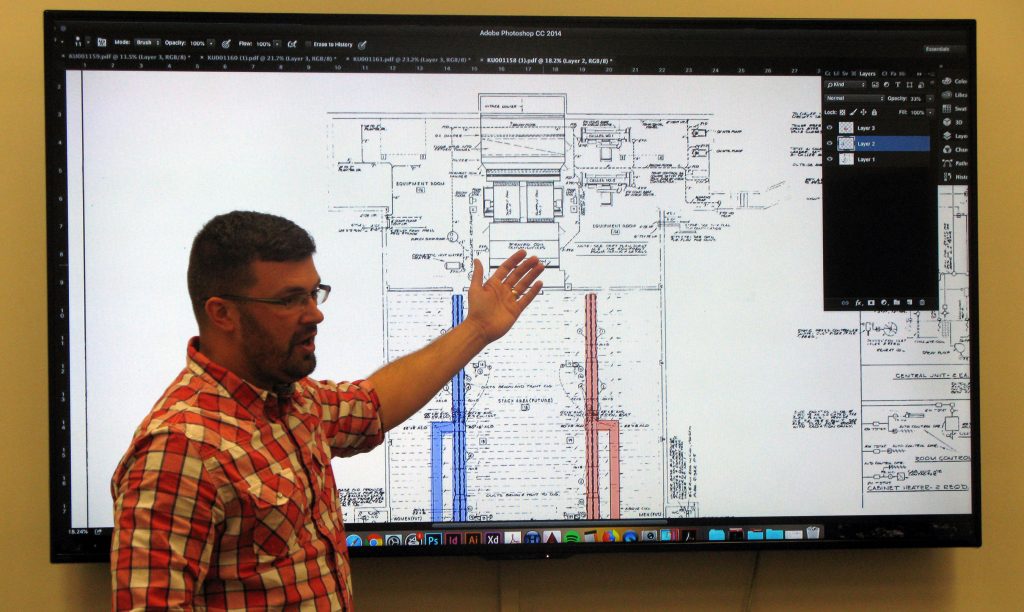
Chris Cameron shows us how air travels from the air handling unit through two underground
channels, which provide air to the east and west sides of the buildings. Click image to enlarge.
It has been a pleasure to work with Chris and Kelly from the Image Permanence Institute. We have learned so much about the idiosyncrasies of our building and have some short-term action items to help its systems operate more efficiently. We will receive a final report from the consultants early next year and will then make plans for next steps.

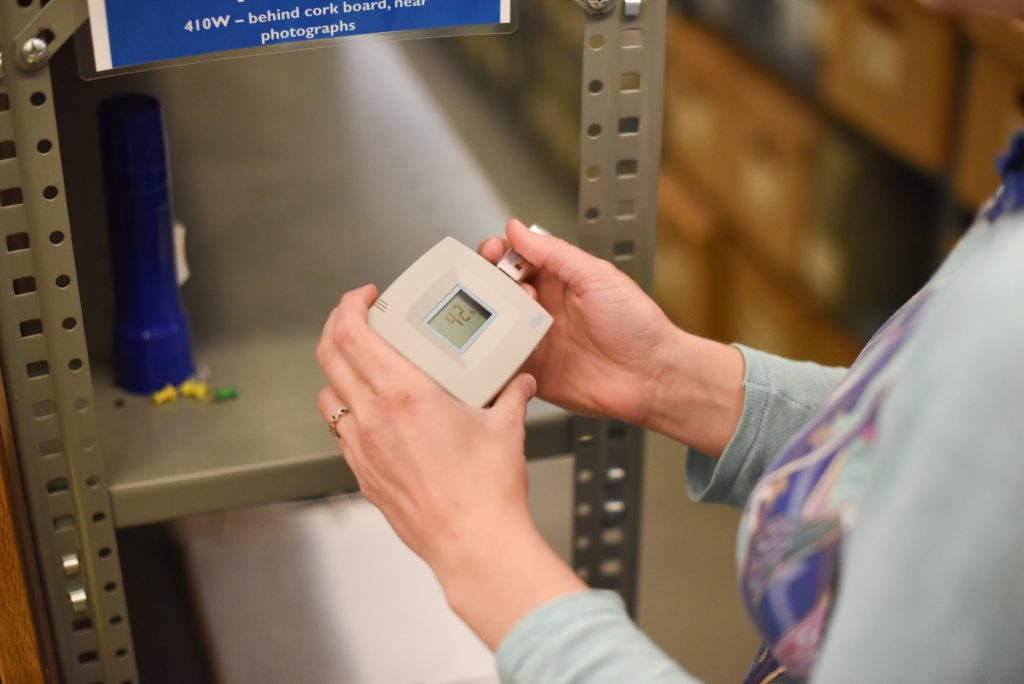
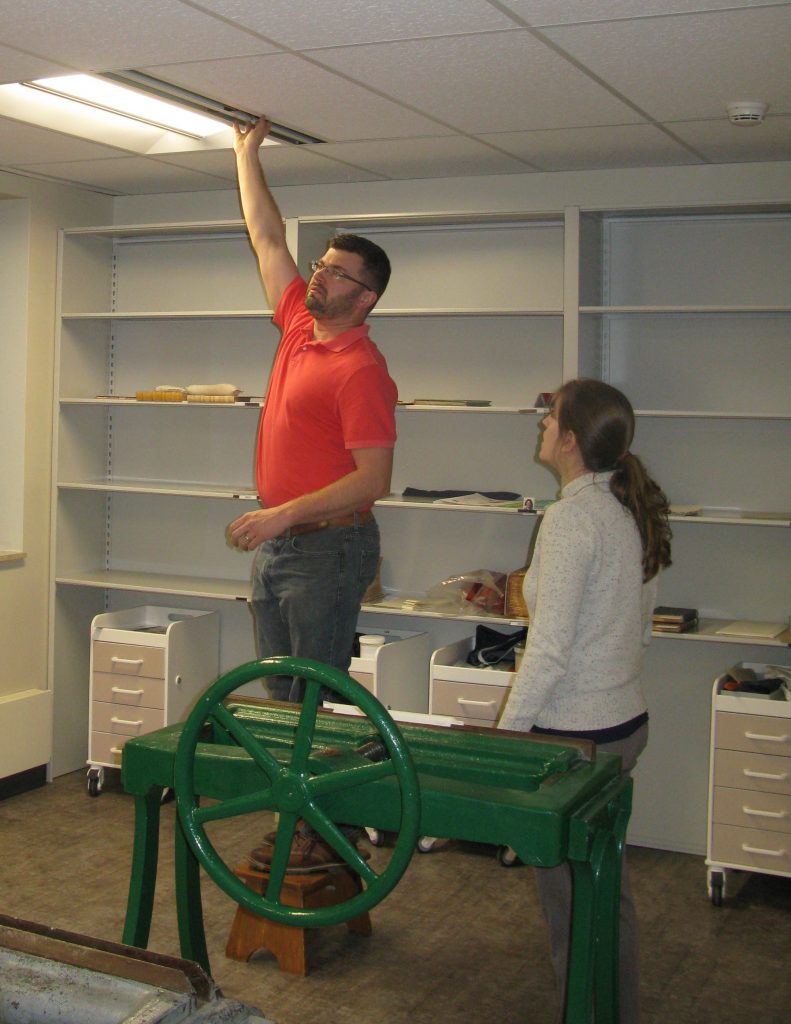
Chris Cameron and Kelly Krish discuss temperature and relative humidity
data for a space in Spencer Library. Click image to enlarge.
Many thanks also to the National Endowment for the Humanities and the grant reviewers who deemed our project worthy of funding. We are most appreciative.
Whitney Baker, Head
Conservation Services
Any views, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this blog post do not necessarily represent those of the National Endowment for the Humanities. “Improving the Physical Environment in Spencer Research Library” has been made possible by a grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities: Sustaining Cultural Heritage Collections.






